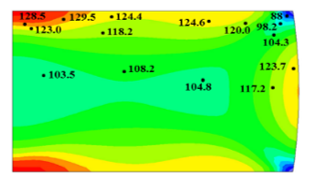
Metallurgical identification of material
Fig. (a) shows predictions of grain size with known material properties and Fig. (b) shows predictions of grain size with material properties calculated by a new material identification scheme, which is based on AFDEX and HyperStudy. The new scheme needs experimental data as input to identify the material. In this study, the experimental input was…
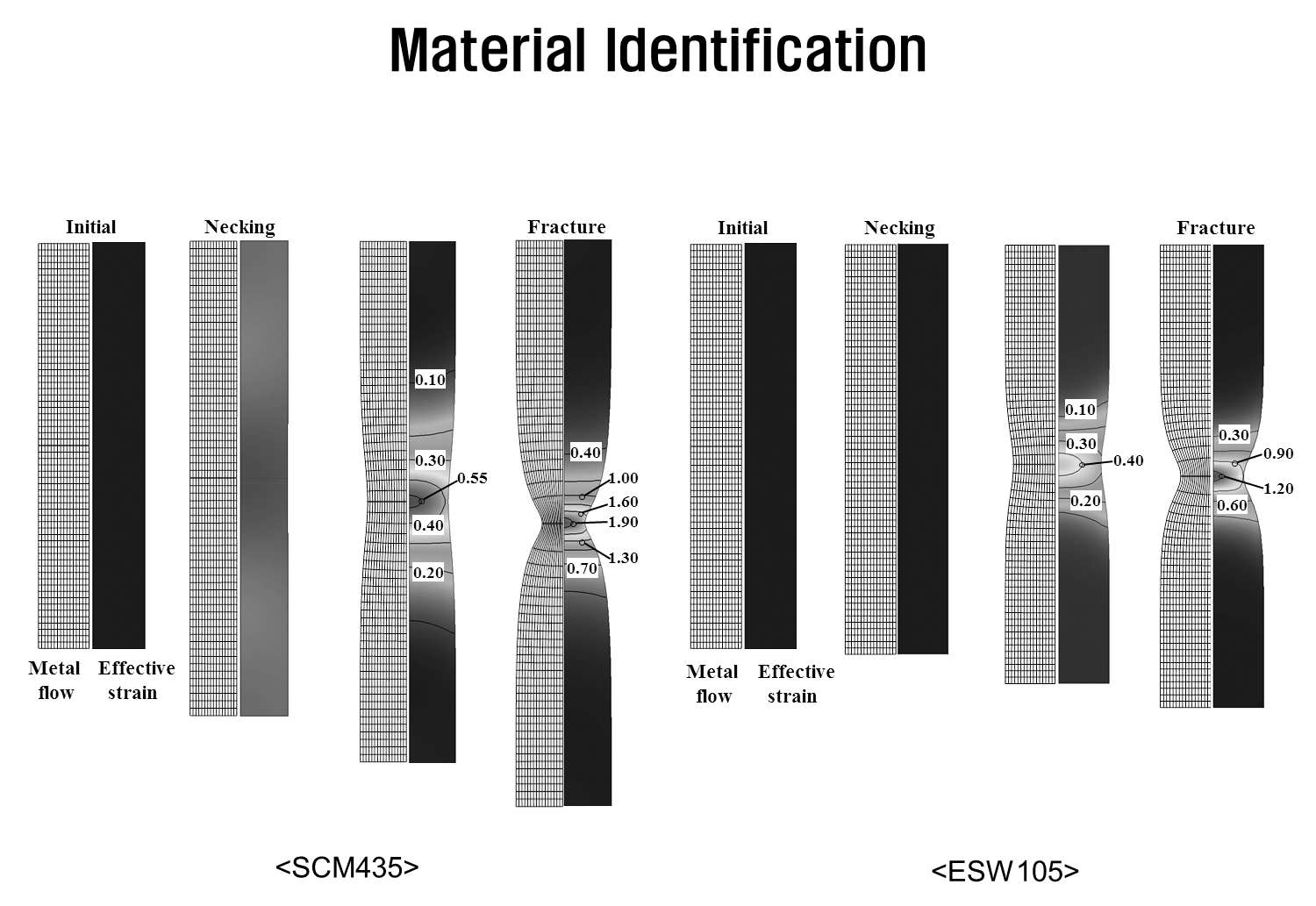
Read MoreDeformation behavior of tensile testing of SCM435 and ESW105
The deformation of tensile specimens was analyzed for two materials, SCM435 and ESW105. It is evident that the strain hardening behavior significantly influences the deformation characteristics and fracture pattern.
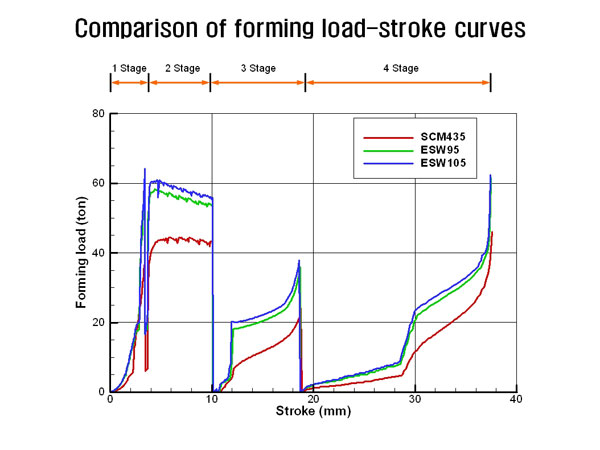
Read MoreComparison of forming load-stroke curves
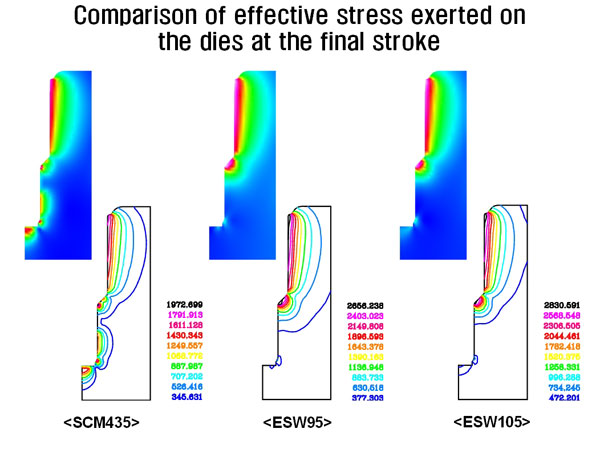
Comparison of effective stress exerted on the dies at the final stroke
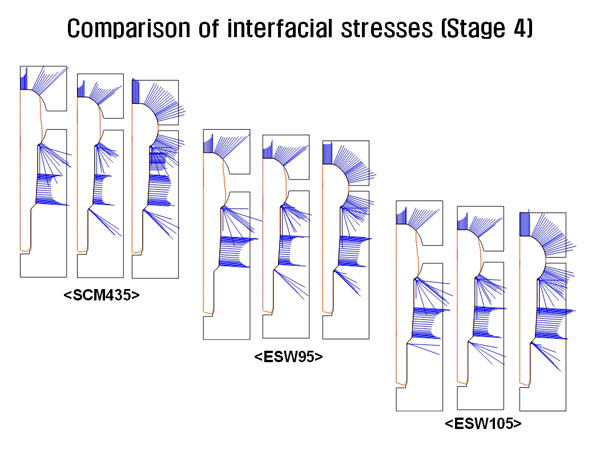
Comparison of interfacial stresses (Stage 4)
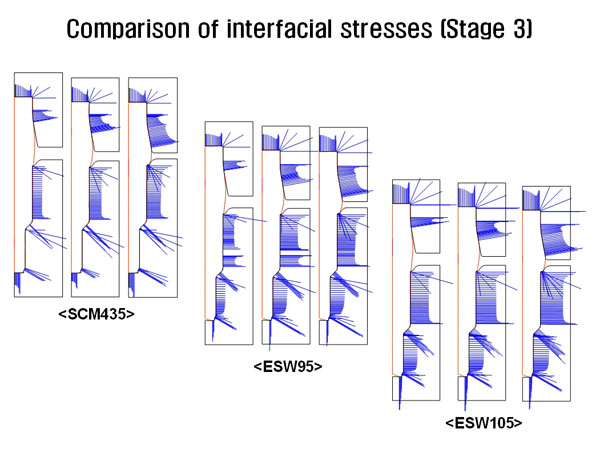
Comparison of interfacial stresses (Stage 3)
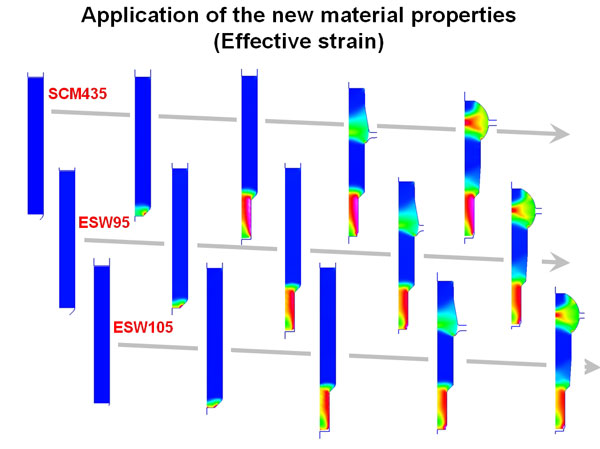
Application of the new material properties (Effective strain)
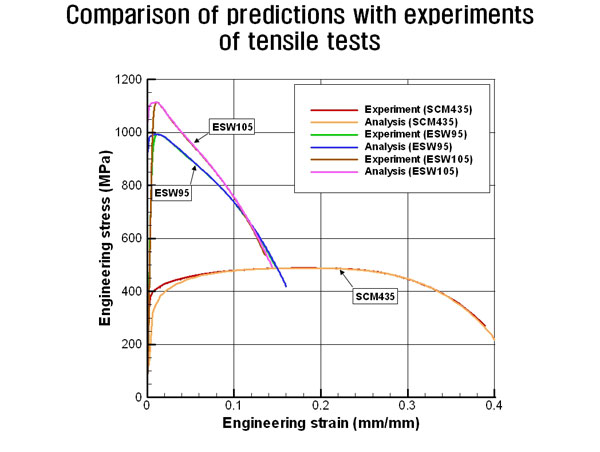
Comparison of AFDEX MAT’s flow stress predictions and experimental data from tensile tests
With the flow stresses obtained by AFDEX MAT, the three tensile tests were analyzed. It was revealed that the predictions are very close to the experiments especially in the plastic region, which implies the accuracy of the approach and AFDEX.
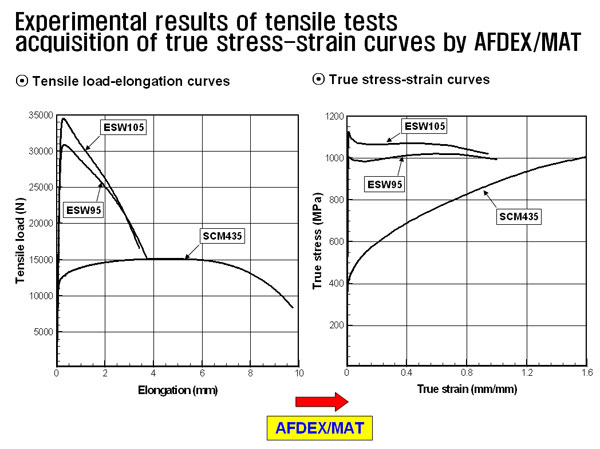
Read MoreConverting engineering stress-strain to true stress-strain curve with AFDEX MAT
Three typical materials, i.e., SCM435, ESW95 and ESW105 were studied to reveal their flow stress information which is one of material properties for plastic deformation simulation. It is interesting to note that SCM435 is a typical strain hardening material while ESW95 and ESW105, Energy Saver Wires, are of high-strength with negligible strain hardening capability. It…
Read MoreTensile test simulation using AFDEX MAT
AFDEX MAT is a material identification module based on tensile test of a cylindrical specimen. With this module, users can obtain flow stresses over large strain for any material (for example, at the strain of 1.5 for mild steels including SCM435, etc.).
Read More